The terms WLAN and Wi-Fi are sometimes used interchangeably, but are actually two separate wireless technologies. If not the same thing as Wi-Fi, this begs the question—what is a WLAN? Let’s discuss its meaning and what makes it different from Wi-Fi.
What is A WLAN?
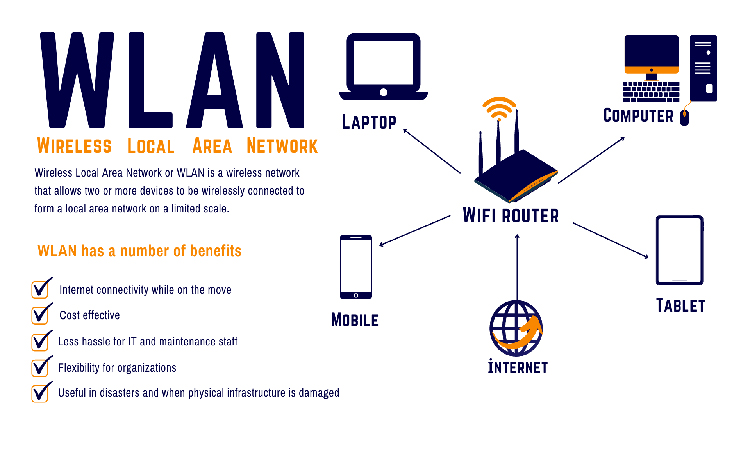
WLAN stands for wireless LAN. A LAN is a Local Area Network contained within a building or campus that represents a geographical or functional construct. It is usually connected via cabling. Common examples of LANs are home Wi-Fi networks and small business networks where several devices are connected to a wired router.
WLAN uses radio technology instead of wiring to interconnect network nodes. These networks may or may not use Wi-Fi. Wireless technology either extends or replaces parts of the LAN or both. A WLAN can be attached to a pre-existent, larger network, such as the Internet.
How do you build a WLAN?
Before attempting to create a WLAN, it’s important to be clear about your goals. What problem is being solved? What applications will be used? This will give an indication on how best to move forward.
Once the requirements have been gathered, the main steps include:
- Identifying which devices will be used as nodes and the operational needs of each. For example, building sensors have different power, security, and bandwidth requirements than tablet PCs.
- Choosing the correct WLAN products and determining what type of LAN connections and wiring the network will need.
- Having a professional wireless technician design the WLAN layout.
- Installing the WLAN components.
- Testing wireless coverage and performance.
- Verifying that the WLAN design meets the operational requirements.
- Identifying system personnel to be responsible for updates, troubleshooting, maintenance, and lifecycle replacements.
Building a WLAN can result in a range of system topologies.
What are the benefits of a WLAN?
WLANs don’t require cable but depend on special-purpose devices such as mobile phones, tablet computers, laptops, gaming consoles, and other internet-enabled home devices and appliances.
The benefits of a WLAN include:
- A WLAN can support a large number of devices.
- The setup for WLAN is easier than laying cables for wired networks.
- It is easier to access a WLAN than a LAN.
- Network costs are saved through the reduction of physical wires and associated pathways.
- WLANs can be built virtually anywhere.
- Device portability and mobility enable new workflows.
- Short-term, temporary networking needs can be addressed more easily.
- Adjustments to the system are generally easier to make than with wired connections.
WLANs are common in businesses, public areas, and homes.
Are there any challenges associated with WLAN?
Despite the benefits of WLAN, there are a few disadvantages:
- Wireless technologies can be affected by interference on the radio spectrum.
- WLAN design and implementation require specific skills.
- Proprietary, non-standards-based technologies can be challenging to support.
- Network and client devices used in WLAN often have varying feature sets that can be difficult to synchronize.
WLAN uses radio technology to connect nodes within a LAN but doesn’t necessarily use Wi-Fi.
What is Wi-Fi and how does it work?
Wi-Fi is a wireless networking technology that uses radio waves to provide high-speed internet access. It uses IEEE 802.11 standards and coverage typically extends to the edge of a wired network.
Wi-Fi is not the same as internet, although the two are closely related and the terms are often used interchangeably. The Internet is a WAN (wide area network) that uses a series of protocols to transmit information between devices and networks around the world. Wi-Fi is a means for connecting devices without having to use cables.
Wi-Fi networks function by using radio frequency (RF) technology, a frequency within the electromagnetic spectrum associated with radio wave propagation. When an RF current is supplied to an antenna, it creates an electromagnetic field that is able to propagate through space. A wireless signal is then broadcast from an access point to network adapter-equipped devices that can detect and use it to establish a connection to the network.
Wi-Fi is a type of WLAN, but is not the only type.
Why is Wireless So Important?
Wireless technology allows information to be transferred from one point to another and enables people to communicate without using cables or wires. It provides speed, flexibility, and network efficiency. Because wireless enhances productivity, dependence on it will only grow over time. This technology gives employees the opportunity to work remotely and is less expensive to install and maintain compared to other network options.
What are the benefits of wireless?
The benefits of wireless include:
- Making users more mobile.
- Real-time information accessibility.
- Ease of installation and set up.
- Minimized need for physical cabling prevents safety hazards.
Wireless is important to businesses, manufacturing, healthcare, commercial real estate, education, and many other business sectors. Many wireless networks can be easily updated to accommodate new technology as it becomes available.
Is PoE a form of WLAN?
PoE is not a form of WLAN but is the most common LAN type.
PoE stands for Power over Ethernet. This technology sends electrical power and data over copper wire. Combining hardware for data transmission and power supply onto the same RJ45 Ethernet connector allows for power transmission over the network cabling. This eliminates the need for a local power source at a device location or for having to run a separate cable for power. 802.11 standards are written for compatibility with 802.3 Ethernet standards.
Although wireless will potentially replace wired in most situations, PoE will continue to play a key role in IT networks inside commercial and institutional buildings. PoE offers labor and equipment cost savings by eliminating the need for installing separate electrical lines and outlets everywhere a device needs to be powered. PoE technology can power wireless access points, LED lighting systems, VoIP phones, surveillance products, industrial controls, and network switches; each, with a single Ethernet cable. Security systems, digital signs, and accuracy monitoring sensors can all benefit from PoE technology.
PoE is also much safer than standard electrical cabling when there is a need to connect to an outdoor source.
Follow – https://techhipo.com for More Updates


